Article Summary 25/12/23
Article title
A chemical agonist and the Golgi-resident lipid PI4P activate STING by inducing transmembrane helix rearrangement
Journal
Immunity
Authors
Conggang Zhang (Tsinghua University)
Tags
cGAS-STING; PI4P; Molecular glue
Introduction
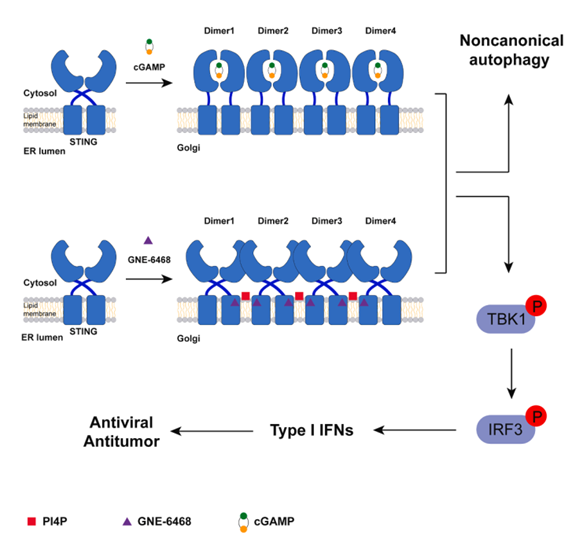
cGAS-STING pathway regulates innate immunity and is potential drug target. In cGAS-STING pathyway, cGAS recognizes dsDNA to produce STING agonist cGAMP, the latter stimulates STING oligomerization at Golgi and activates the downstream cascade reaction to trigger immunity pathway. Recently, the phospholipid PI4P was reported to activate STING pathway but the mechanism of how PI4P activates STING is yet elusive.
This work
Through screening the STING-activating phenotype using a small molecular drug library, GNE-6468 was discovered and found to be an agonist of STING-induced innate immunity in cell. Next, they analyzed the cryo-EM structure of GNE-6468 bound to STING and found GNE-6468 bound a new binding pocket formed by two STING dimers. Surprisingly, densities of PI4P was found in complex structure, indicating PI4P as a molecular glue to stimulate oligomerization of STING.
Next, they performed detailed structure analysis and found GNE-6468 caused ~9.6 angstrom shift of STING transmembrane helix 2 and 3, which is orthogonal to other STING agonists. Inhibitors targeting TM2/3 suppressed the stimulation of GNE-6468 towards STING. Moreover, mutation assays suggested that both the interaction PI4P and GNE-6468 with STING were indispensable for STING oligomerization and activation.
Subsequently, they found PI4P was essential for GNE-6468 activating STING in cell, and verified the drug effect of GNE-6468 to model cells and mice of anti-cancer.
In summary, this article accidently found PI4P acts as a molecular glue to confer binding between GNE-6468 and STING. Also, the new molecule GNE-6468 was found to be an attractive STING-target agonist drug. However whether there is endogenous factors regulating PI4P-STING interaction was not clear.
doi
10.1016/j.immuni.2025.11.004