Article Summary 7/5/25
Article title
Isoform-specific function of NSD3 in DNA replication stress confers resistance to PARP inhibitors in prostate cancer
Journal
Molecular Cell
Tags
PARP inhibitors; Drug resistance; Prostate cancer
Introduction
mCRPC is a lethal cancer that belongs to prostate cancer (PC). Large fraction of mCRPC patients are shown genomic anomaly, especially in DNA repair related genes. PARP inhibitors have been employed to treat such DNA-repair deficient cancers. However, clinical trial of PARP1 towards mCRPC exhibited drug resistance with unknown mechanism. How mCRPC generates PARPi drug resistance remains elusive.
This work
First, to discover the dark matter in mCPRC drug resistance towards PARPi, the article searched the mCPRC-relevant deleterious gene in patient database and searched human reference interactome to seek potential regulators. NSD3, a methyltransferase family, containing 2 paralogues NSD3S and NSD3L, is targeted. Through overexpression of NSD3S in cells, they found NSD3S confers drug PARPi resistance to PC cells. As well, they found that PARPi-resistant PC cells showed high NSD3S level, and knockdown of NSD3S significantly raised the sensitivity towards PARPi. In addition, PROTAC targeting of NSD3 also weaken the drug resistance. They then expanded the usage of PROTAC-PARPi to mouse model and found PROTAC-PARPi combination strategy robust for NSD3S-abundant PC cells.
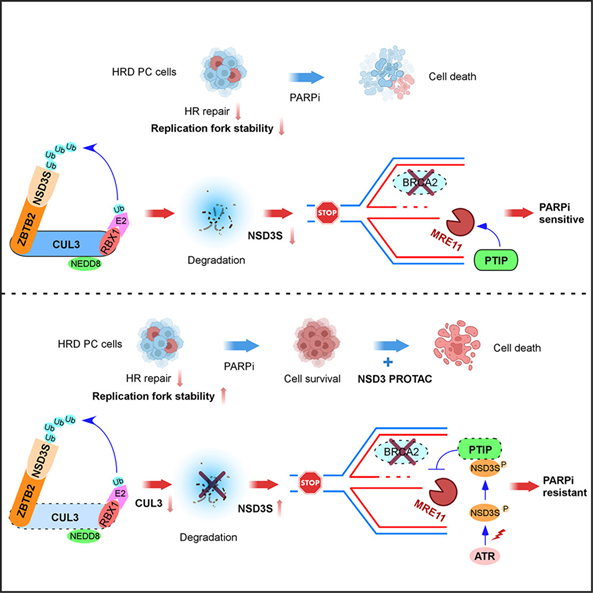
To explore why NSD3S is highly abundant in PARPi-resistant PC cells, they performed IP-MS and found CUL3^TBZB2^ E3 complex responsible for ubiquitination degradation of NSD3S. In PARPi-resistant cells, CUL3^TBZB2^ E3 is low abundant and thus unable to sufficiently degrade NSD3S.
Next, to explore the mechanism by which NSD3S used to escape PARPi, they revealed NSD3S is phosphorylated and recruited to DNA replication fork and stabilizing the fork. Binding of NSD3S to replication fork requires PT1P, which generates a competition between NSD3S and nuclease MRE11 (which also requires PT1P to bind replication fork), thus preventing sufficient digestion of replication fork by MRE11.
Finally, they systematically evaluated the relationship between NSD3S level in cell and PARPi resistance. They also searched the NSD3S-PARPi resistance relationship in ovarian cancer patients. They claimed NSD3S is competitive for playing as a PARPi resistance biomarker.
doi
10.1016/j.molcel.2025.06.004