Article Summary 5/24/25
Article title
TOM20-driven E3 ligase recruitment regulates mitochondrial dynamics through PLD6
Journal
Nature Chemical Biology
Tags
CRLs E3 ligase family; mitochondria dynamics
Introduction
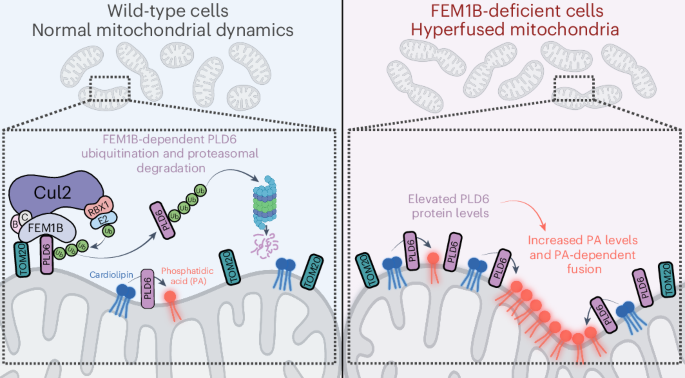
Dynamics of mitochondria is intricately regulated. UPS-involved protein quality control regulates the level of mitochondria dynamic-related proteins. UPS involves E1/E2/E3 cascade enzymatic system in which E3 determines substrate specificity. CRLs complex family stands for the largest E3 family. CRL2 complex adapts different substrate receptors to engage different substrates, leading to UPS of different substrates. FEM1B is a CRL2 substrate receptor which recognizes ψ-Pro/C-degron and Cys-degron. FEM1B-deficient cells show dysfunction of mitochondria, however the full substrate scope of FEM1B on mitochondria function does not clear. How does FEM1B regulate mitochondria dynamics?
This work
To address this question, this work performed FEM1B-KO proteomic analysis and found PLD6 as CRL^FEM1B^ UPS degradation substrate. Cellular, biochemical and structural analysis revealed FEM1B degron-binding pocket bind PLD6 C-tail to promote its degradation. Next, they demonstrated FEM1B affects PLD6-mediated mitochondria dynamics. But does other factors affect FEM1B targeting mitochondria membrane? This work focused on mitochondria OM complex subunit TOM20. It co-locates with FEM1B and cells with TOM20 siRNA failed to locate FEM1B on mitochondria. Structural analysis indicated TOM20 interacts with FEM1B through hydrophobic interactions. Abortion of interaction abolished the regulation of FEM1B towards PLD6 level and mitochondria dynamics.
Collectively, this work combined structural (cryo-EM), proteomics, cellular and biochemical approaches to depict the TOM20-FEM1B-PLD6 pathway in mitochondria dynamic regulation. However, why FEM1B recruitment on mitochondria is dependent on TOM20 but not PLD6, which also interacts with FEM1B, remains unknown. I hypothesized the abundance of TOM20 and PLD6 on mitochondria membrane is pivotal for the primary regulation determinant for FEM1B recruitment on mitochondria, or the two set of interactions are not sufficiently relevant. More exploration is needed to clarify the relationship between these interactions and why FEM1B recruitment is determined by TOM20 but not PLD6.
doi
10.1038/s41589-025-01894-4