Article-summary-1-19-25
Article title
Bidirectional histone monoaminylation dynamics regulate neural rhythmicity
Journal
Nature
Tags
Histone PTMs; Metabolic PTMs; Genetics
Introduction
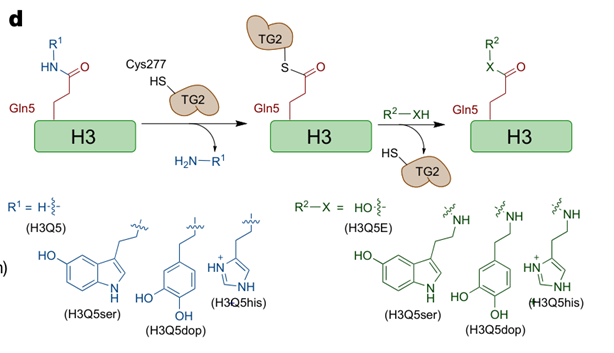
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) regulate chromatin-templated processes such as chromatin spatial organization and transcription to determine cell fate. Monoaminylation on histone H3 stands for a PTM that attaches a monoamine neurotransmitter such as dopamine and serotonin. Monoaminylation regulates neural transcription related processes. Previously discovered H3 monoaminylation is induced by TG2 enzyme, whereas the erasing mechanism and relationship among different H3 monoaminylations remains unknown.
This work
The article adapted chemical biology approaches such as metabolite labeling by CuAAC clicking reaction and in vitro monoaminylation assay using synthetic peptide, showing that TG2 works as a H3Q5 monoaminylation writer, eraser and exchanger, regulating different H3Q5 monoaminylation.
In addition, a new monoaminylation is discovered, that is, H3Q5his (histamine). H3Q5his could antagonize WDR5 (an H3K4 binder to write H3K4 methylation) binding towards chromatin. H3Q5his could also regulate neural rhythmicity according to cellular experiment performed by this work.
doi
10.1038/s41586-024-08371-3