Article-summary-11-09-24
Article title
Structure-guided discovery of bile acid derivatives for treating liver diseases without causing itch
Journal
Cell
Tags
Cryo-EM structure, Drug rational design
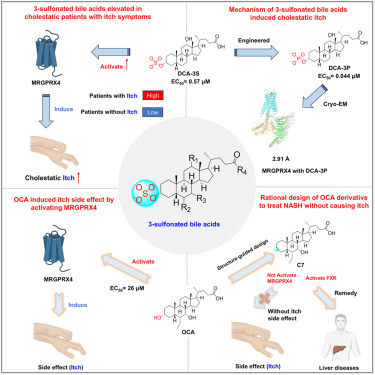
Introduction
NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) gains increasing attention as its prevalence in liver disease patients. Although no FDA-approved drug discovered for NASH, first in class bile acid derivative agonists targeting FXR receptors such as OCA have been investigated to treat such diseases. However, OCA causes cholesteric pruritus (itch) in clinical trials. Hitherto no approach has been suggested to overcome the adverse effect of itch. New leading compound is needed to be discovered to overcome OCA-induced itch.
This work
Through cryo-EM, molecular dynamics, biochemical and cellular assays, the structural mechanism of how bile acid derivatives stimulates their itch-related acceptor, hX4, was demonstrated. bile acid derivatives utilized their acidic functional group (sulfurylated and phosphorylated) to recognize hX4 basic pocket. Based on the structural observation, a new compound named C7 was designed to prevent binding of itch-related receptor hX4 but retaining drug effect for liver diseases in organism models and rat models.
doi
10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.001