Article summary 8/27/24
Article title
Bridging of DNA breaks activates PARP2–HPF1 to modify chromatin
Journal
Nature
Tags
Nucleosome; PARP1; Cryo-EM structure
Introduction
To respond DNA strand break, PARP1 and its paralogue PARP2 assemble at chromatin and ADP-ribosylate (ADPr) histones. PARP-mediated histone ADPr relies on cofactor HPF1, which switches PARP1 residue preference from Glu/Asp to Ser. ADPr chromatin then recruits downstream effectors to promote DNA repair pathway. However, the mechanism of PARP enzymes recognizing chromatin DNA breaks remains elusive.
This work
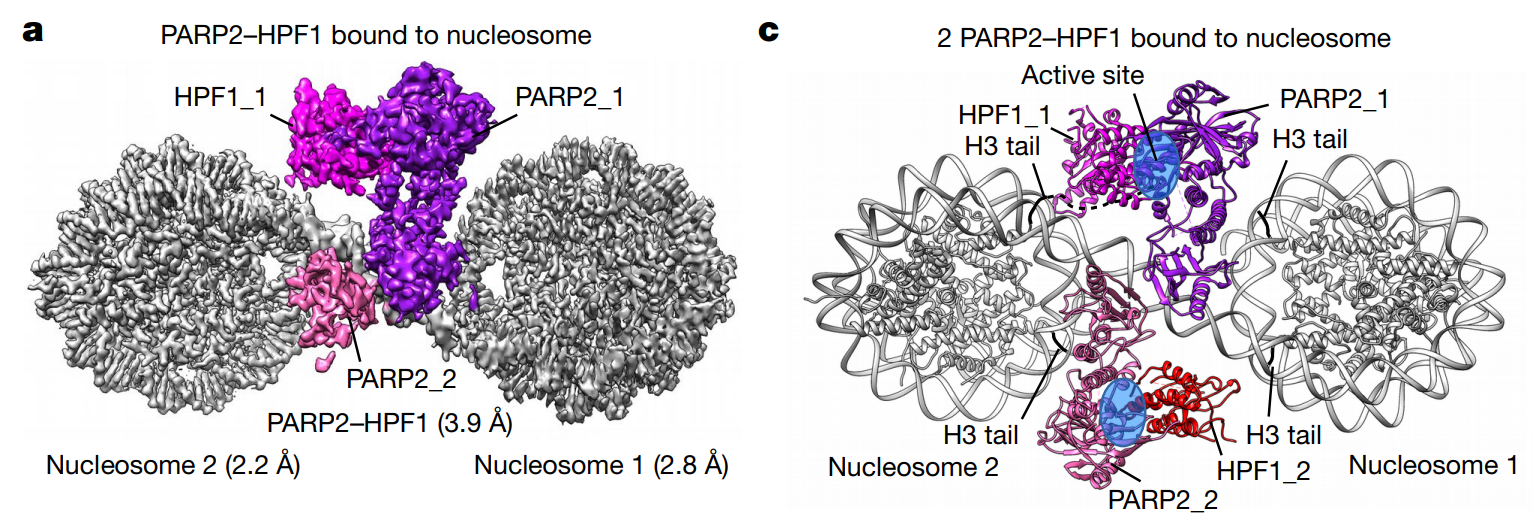
I. Determine the cryo-EM structure of PARP2/HPF1 bound to nucleosome. PARP2/HPF1 forms 2:2 complex with nucleosome. Local focused classification is used to raise resolution: 2.2Å and 2.8Å resolution for 2 NCPs, 3.9Å for PARP2/HPF1.
II. Analysis of interaction surface. PARP2 WGR domain interacts with DNA double strand break, that is, the internucleosomal connection site of the two linker DNA. PARP1 HD domain interacts with nucleosomal DNA, while HPF1 loop lysines interacts with SHL-7 and 7 DNA on another nucleosome. HPF1 mutation affects complex formation, which is visualized by native-PAGE.
III. Interaction between DNA break and PARP2. Through native-PAGE and in-gel ADP-ribosylation assay, they confirmed that DNA break bridging could activate PARP2 self-catalysis activity. Also, DNA-binding defect PARP2 mutant is less prone to form ternary complex and modify H3. Comparing the prior-activated PARP1/DNA complex, both HD helix and signal loop shifted, indicating the cascade-triggered conformation change-caused PARP2 activation upon NCP binding.
IV. Hypothesized PARP2/HPF1 catalytic cycle. Two more conformations are resolved, demonstrating two more open state (at active site) that accommodate H3 tail entry.
V. Hypothesized overview ADPr mechanism. Found that PARP2/HPF1/NCP complex dissociates gradually after NAD+ addition. Enhanced PARP2 auto-modification after histone ADPr. Proposed mechanism: first ADPr histone to recruit downstream effectors, then auto-ADPr to disassembly the PARP2/HPF1/NCP ternary complex.
doi
10.1038/s41586-020-2725-7
Article title #2
Dual function of HPF1 in the modulation of PARP1 and PARP2 activities
Journal
Communications biology
Tags
Biochemistry; PARP1
Introduction
PARP1 and PARP2 are of same PARP family enzymes while PARP1 possesses 3 more zinc fingers, which bind DNA. PARP1 and PARP2 exhibit distinct activity behaviors. How co-factor HPF1 regulates PARP1 and PARP2 catalytic activity on nucleosome as well as auto-modification remain largely unexplored.
This work
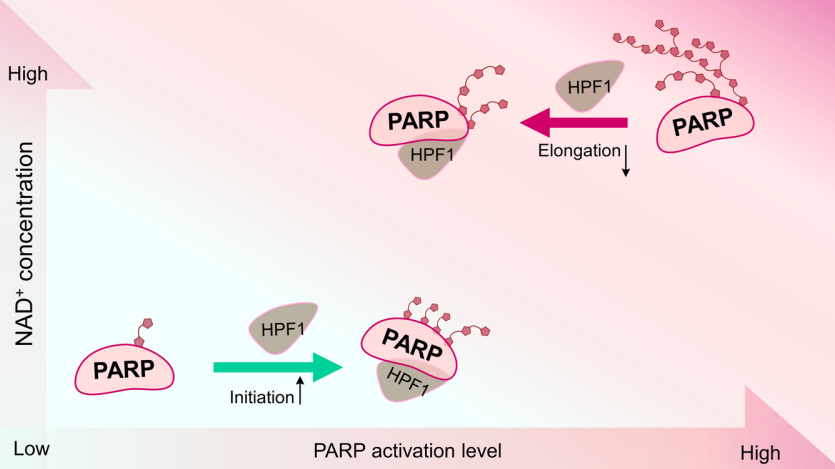
This work explored how HPF1 activates PARP1 and PARP2. Using autoradiograms, they found that HPF1 stimulates PARP1/2 auto-modification as well as histone ADP-ribosylation. However the stimulation is limited to a defined range (about 0.5-2eq PARP1) while too high HPF1 concentration leads to declined ADPr chain length. In addition, NAD+ concentration also affects ADPr chain formation.
Overall, PARP1 and PARP2 hardly distinct from each other in catalytic behavior combined with HPF1. However PARP1 and PARP2 have different intrinsic activity towards themselves or nucleosome substrates.
Autoradiogram gels seem smear and heterogenous.
Hydroxylamine is used to cleave Asp/Glu-modified ADPr chain.
doi
10.1038/s42003-021-02780-0
Article title #3
Serine ADP-Ribosylation Depends on HPF1
Journal
Molecular Cell
Tags
Biochemistry; PARP1; Nucleosome; MS
Introduction
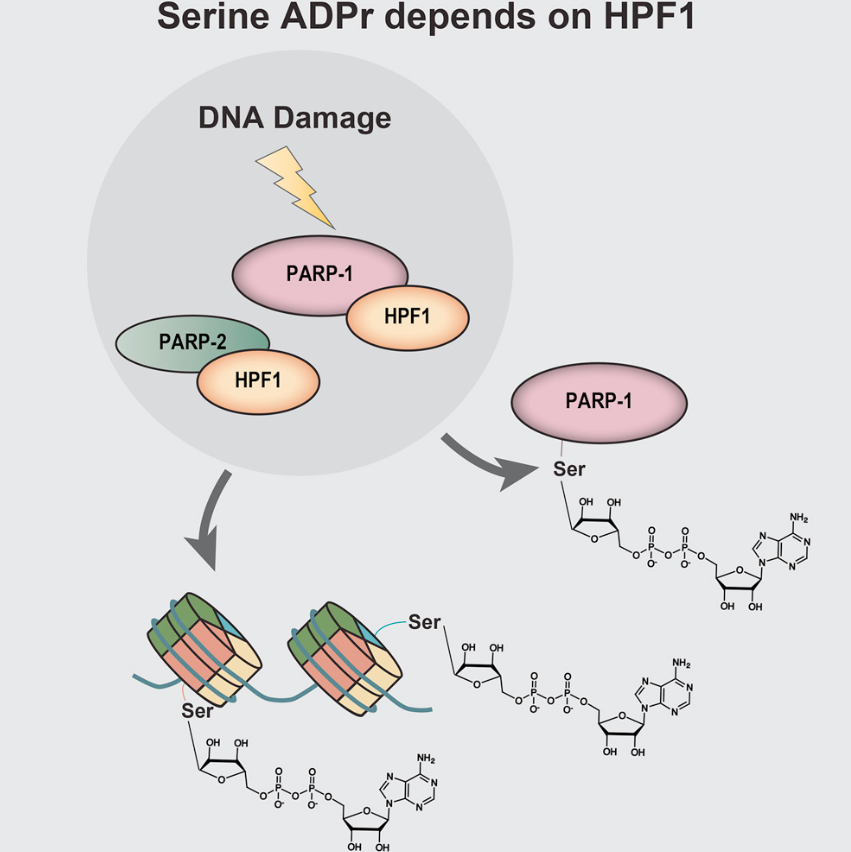
PARP1 is the major enzyme catalyzing histone ADPr modification. Previously, histone serine-modification is found in DNA damage response while HPF1 is found to be PARP1 co-factor and helps PARP1 ADP-ribosylate histones. However, the chemical basis of PARP1-catalyzed histone ADPr is yet unknown.
This work
Using SILAC-based unbiased MS analysis, they extracted cell histones and found the ADPr modification sites. As well, they found that histone ADPr relies on HPF1.
Reconstitution of PARP1/HPF1 activity on H3/H4 tetramer, recombinant histone or histone peptides are performed, using autoradiogram. Nudix is used to cleave poly-ADP-ribosylation to single ribose phosphate which enables MS analysis.
In addition, PARP1 auto-modified serine is also scanned. H1 is also proved to be PARP1 substrate in vitro. Notably, H2A and H4 N terminal serines are shown ADPr modified in vivo.
doi
10.17632/pmvv5mdmrm.1