Article summary 8/23/24
Article title
Structure and repair of replication-coupled DNA breaks
Journal
Science
Tags
DNA replication; Next generation sequencing
Introduction
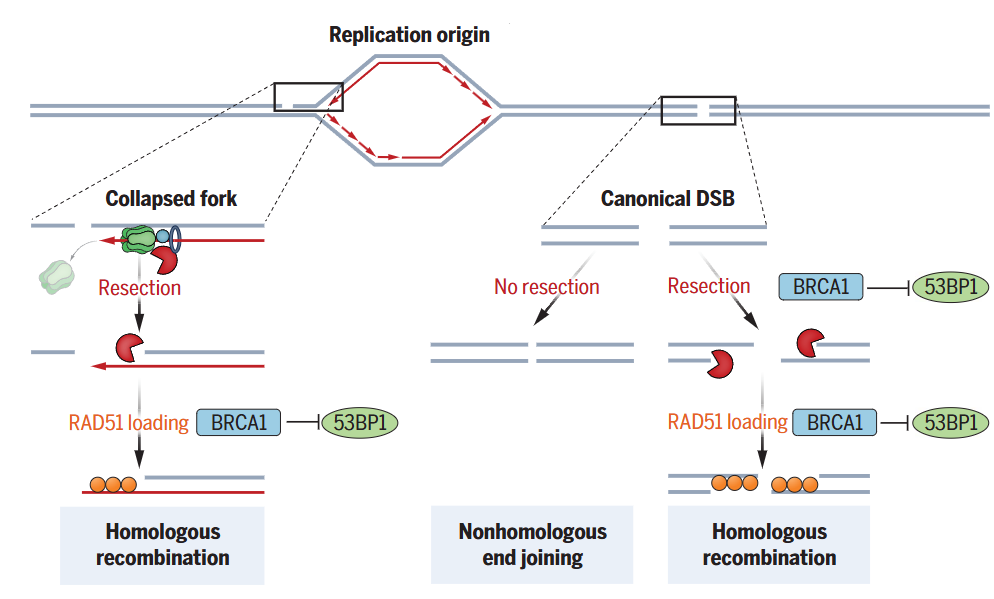
DNA strand break is repaired in cellular processes. Unrepaired DNA breaks affect genome integrity. In cell division S phase, DNA single strand nick causes bypassing DNA replication fork stall and collapse. Recent reports showed that DNA single strand nick was converted to double strand break after fork collapse, triggering HR pathway to repair the break. However, how DNA replication fork behaves to convert DNA single strand break signal to HR pathway remains unknown.
This work
Utilizing Cas9 technology to produce single strand nick at specific site, while using next-generation sequencing (END-seq) to label DNA double strand and resection. They found that leading and lagging strand produces distinct double strand break form (seDSB and deDSB), in which RAD51 knockoff affects not only the DSB type but also DNA resection. In addition, BRCA1 and 53BP1 are found to antagonizingly regulate RAD51 loading on fork collapse.
Overall, genetic and sequencing approaches are applied to observe crosstalks among DNA replication, single strand nick and homologous recombination.